In this quick guide we demonstrate how to get started with the VisionLib SDK for Unity3D. We provide a broad overview on the Unity SDK, the workflow with VisionLib, and the structure of tracking configuration file.
There is also a step-by-step video for this tutorial on our YouTube channel:
Before you start, be sure to have the following installed or at hand:
Assets/Import Package/Custom Package.. and import the vlUnitySDK_XX.Y.Z.unitypackage file into your empty projectVisionLib/Examples/ModelTracking/SimpleModelTracking in the project navigator and open SimpleModelTrackerExample.unityStreamingAssets folder of your Unity projectIf it is named license.xml, you are already done. Otherwise, select the VLCamera under VLTracking in the hierarchy and specify the license file name and path at the License File property of the VLWorkerBehaviour in the inspector window.
Start button.The example scene lets you select your camera at start.
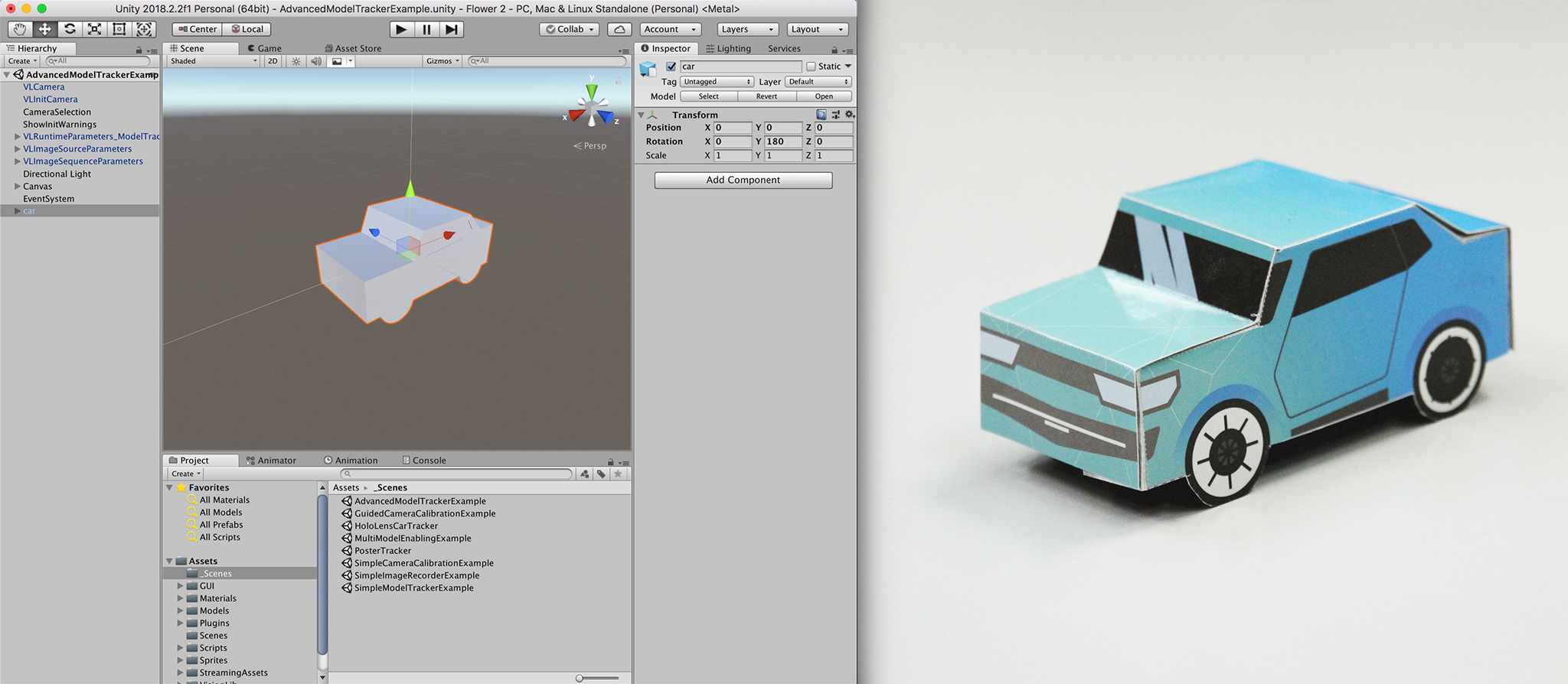
You should see the live camera view and a 3D model of the mini car in Unity's game window now.
If everything worked well, your game view should look like in the picture above.
For demonstration purposes, we merely superimpose the same 3D model that is used for tracking the real mini car in the live image stream. But of course, you can replace this simple augmentation by anything more complex. For this you can exploit the full range of features that Unity3D offers to you. In contrast to other tracking techniques, model tracking will always use the physical 3D model as a reference. As an advantage, all augmentations will appear right in place as soon as the real object is recognized and tracked in the images, because the coordinate systems of the tracking system and the created virtual content are aligned automatically.
Controlling and customizing the tracking can be done via JSON-formatted configuration files. Within these files you can change tracking targets, fine-tune the tracking parameters, or specify camera or image stream inputs. There exists a pre-configured file for this quick-start demo, which you can use as a starting-point and adapt it to your needs.
For changing the 3D model you can do the following.
In order to track another model, you need:
In our case, we replace the mini car with a sports car model. To do so:
Models folder of your project; we will use this for superimposition.StreamingAssets/VisionLib/Examples/ModelTracking folder; this is used for tracking.Inside this folder, find the car.vl file, create a backup and edit the original. This is the tracking configuration file, which is in JSON format. Please open the file in a text editor and review it there.
tracker section, look for modelURI and change car.obj (which is the mini car's 3D model) to sports_car.obj (which is the reference to the new tracking model we've copied into the folder).Please note the metric parameter. Here, you should define in which scale your 3D model was created. In our case both, the mini car model and the new sports car, are modeled in m. Change this to mm or cm, if your metrics differ.
SceneContent, disable the Car model.We don't want to use the old model for visualization, but the new one instead. To do so, we need to add it to the scene.
Model folder.VLInitCamera prefab under VLTracking in the hierarchy.This camera defines the model's initial pose that you could see, once the Start button was pressed. Right now, the camera is set nicely for the old mini car model. We need to change this pose, in order to fit the new model. With the camera selected, move it until you get a nice sight on the new model (have a look at the camera preview window in the image above). This position defines where your tracking — and respectively your users later on — should start working with the augmented reality.
Start button. The new model should now be rendered as you've defined its init pose via the VLInitCamera.In order to understand what VisionLib's computer vision engine is doing, press the Debug on button. You will now see two more windows on the screen. One is revealing a gray-scale image with 'jaggy' lines, representing the ongoing 3D model's edge detection. The second window prints some statistics regarding tracking parameters that are defined in the configuration file.
Hey, hey! You just tested VisionLib's 3D model tracking and exchanged the demo model.
If this does not work with your model, we recommend reading through the following sections in order to set the parameters right for your tracking case.
Perhaps you might have noticed some text, stating that your camera has not been calibrated. This is a crucial task, which improves the tracking experience a lot. So for the next step we do recommend calibrating your camera. Therefore, follow this tutorial: Camera Calibration.
If you want to dive a bit deeper in how to configure the model tracker, we recommend reading the detailed Model Tracker Tutorial, which shows you how to set up a scene from scratch. It also explains VisionLib's prefabs, debug options, and how to work with coordinate systems for VisionLib and Unity in detail.